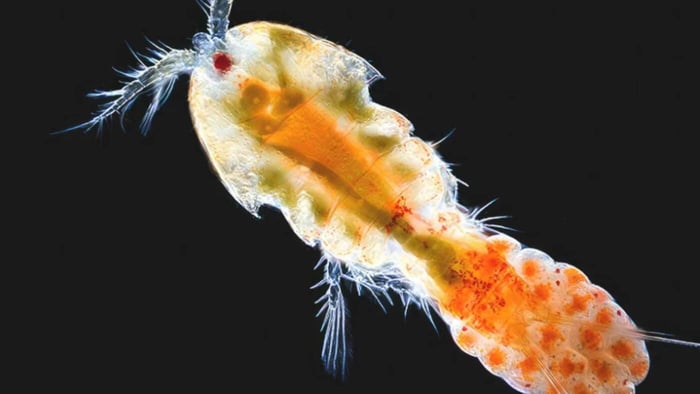
What Are Live Copepods?
In the hidden realms of our oceans and aquatic ecosystems, live copepods are unassuming yet remarkable creatures that play crucial roles in maintaining the health and balance of aquatic life. These tiny crustaceans, often overlooked by the casual observer, serve as an essential link in the marine food web. Join us as we dive into the captivating world of live copepods, uncovering their significance, diversity, and relevance in aquariums and marine environments.
The Basics of Live Copepods
Copepods are small, planktonic crustaceans belonging to the subclass Copepoda. They are incredibly diverse, with thousands of species inhabiting freshwater and marine environments across the globe. What sets live copepods apart is their pivotal role in marine ecosystems as both consumers and prey.
Size Matters: Live copepods typically range in size from 0.2 to 2 millimetres, making them barely visible to the naked eye. Their diminutive stature belies their importance in the marine food chain.
Diverse Species: Various species exhibit distinct adaptations to their specific environments within the copepod family. Some are pelagic, living in open waters, while others are benthic, residing on the ocean floor or attached to substrates.
Reproductive Prowess: Copepods are renowned for their prolific reproductive capabilities. Females can produce hundreds or even thousands of eggs, contributing significantly to their abundance in aquatic ecosystems.
The Ecological Significance of Live Copepods
Copepods are the unsung heroes of marine ecosystems, serving as a vital link between primary producers, such as phytoplankton, and higher trophic levels, including fish and marine mammals. Their diet typically consists of phytoplankton, detritus, microalgae, and other copepods.
Phytoplankton Grazers: Pods are voracious consumers of phytoplankton, microscopic photosynthetic organisms. By feeding on phytoplankton, copepods help regulate its population, preventing harmful algal blooms that can disrupt marine ecosystems.
Nutrient Cycling: These tiny crustaceans also contribute to nutrient cycling by processing detritus and organic matter in the water column. This helps maintain water quality and supports the growth of other marine organisms.
Forage for Fish: Copepods serve as a critical food source for various marine species, including larval fish and filter-feeding organisms like corals and clams. Their nutritional value makes them a cornerstone of the marine food web.
Live Copepods in Aquariums
Aquarists and marine enthusiasts have recognized the value of live copepods in maintaining healthy reef aquariums. Adding live pods to an aquarium can:
Promote Natural Behavior: Pods provide a natural food source for many aquarium inhabitants, encouraging natural foraging and hunting behaviours.
Nutrient Control: They assist in nutrient control by consuming excess phytoplankton and detritus, reducing the risk of nutrient imbalances and algal blooms.
Biodiversity: Introducing copepods enhances biodiversity within the aquarium ecosystem, supporting a more balanced and resilient environment.
Reef Health: In reef aquariums, live copepods can help sustain corals and other filter-feeding organisms by providing a continuous source of small prey.
Conclusion
Live copepods may be small, but their significance in marine ecosystems and aquariums cannot be overstated. As key players in nutrient cycling and a crucial food source for countless marine species, copepods serve as the invisible threads that weave the intricate tapestry of aquatic life.
Whether in the wild or within the glass confines of an aquarium, these tiny crustaceans remind us of the interconnectedness of all life forms in our oceans, highlighting the importance of protecting and preserving these delicate ecosystems for future generations.
So, the next time you gaze into a marine aquarium or dip your toes into the ocean, take a moment to appreciate the remarkable world of live copepods and the vital roles they play in our watery wonderland.